How Accurate Is A Polygraph Test?
How Accurate Are Lie Detector Tests?
Thanks to the widespread use of lie detectors in television shows and movies, the polygraph test has developed a reputation in pop culture these days. However, while they are used in criminal investigations as well as in the business world, they are not as cut and dried as the crime dramas of the day make them out to be.
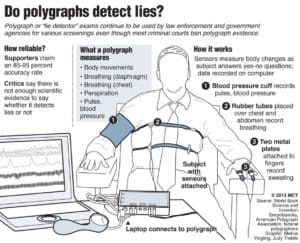 Although called a lie detector, the instrument is not actually able to tell whether or not a person has told a lie. Instead, it is designed to read certain responses of the body. When coupled with specific types of questions and interpreted by a trained expert, these instruments can be used to determine if a person is behaving in a deceptive manner.
Although called a lie detector, the instrument is not actually able to tell whether or not a person has told a lie. Instead, it is designed to read certain responses of the body. When coupled with specific types of questions and interpreted by a trained expert, these instruments can be used to determine if a person is behaving in a deceptive manner.
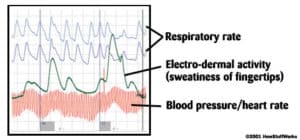
There are three different types of responses that are recorded by lie detectors, or polygraphs as they are more accurately called. The first indicator that is measured is the heart. The rate and blood pressure are recorded in real time to determine when it is spiked by specifically chosen factors.
Additionally, the rate of respiration is recorded for the polygraph. The modern instrument in use takes advantage of a pneumograph. This unit is wrapped around the chest of the test subject and is able to record not only rate of respiration but also the depth of the breaths that are taken. This provides even greater detail regarding their reaction to the questions that are presented on the test.
Lastly, a skin conductivity response is recorded via specialized electrodes which are connected to the fingertips of the test subject. These check the electrodermal response or galvanic skin of the subject and can provide additional information to be interpreted by the examiner.
 The person who is conducting and interpreting the test will then have to take the information and utilize all of the readings in conjunction with the questions in order to determine if the subject was deceptive in answering the questions.
The person who is conducting and interpreting the test will then have to take the information and utilize all of the readings in conjunction with the questions in order to determine if the subject was deceptive in answering the questions.
The training of the examiner is one of the critical components in ensuring the best results possible of the tests that are used. This is because the tests don’t actually detect lies so it is critical that the examiner is able to accurately interpret the levels and types of deception. There are some questions as to how possible that is with some people due to the way the test questions work.
Several types of questions may be presented during a polygraph exam. One type of question always addresses the relevant issue(s) for conducting a polygraph. Another type of questions may address a person’s history, lifestyle, and general trustworthiness. Another type of questions addresses general facts known to be true. Yet another type of questions may address general facts known to be false. Another potential type of question that may be asked addresses the examinee’s understanding of the polygraph. Specific question selection and type of questions are based on the type of polygraph administered.
Three possible outcomes exist when conducting a polygraph evaluation. If the PDD (psychophysiological detection of deception) results indicate no deception, the result will show No Deception Indicated (NDI) or No Significant Response (NSR). If the PDD results indicate deception, the result will show Deception Indicated (DI) or Significant Response (SR). If PDD results fail to meet either the threshold criteria for NDI/NSR or DI/SR then an Inconclusive (INC) results. Obviously, an inconclusive result yields an inaccurate outcome.
According to research noted by the American Polygraph Association (APA) website on polygraph validity:
“The data show that techniques intended for event-specific (single issue) diagnostic testing produced an aggregated decision accuracy of 89% (confidence interval of 83% – 95%), with an estimated inconclusive rate of 11%. Polygraph techniques in which multiple issues were encompassed by the relevant questions produced an aggregated decision accuracy of 85% (confidence interval 77% – 93%) with an inconclusive rate of 13%. The combination of all validated PDD techniques, excluding outlier results, produced a decision accuracy of 87% (confidence interval 80% – 94%) with an inconclusive rate of 13%. These findings were consistent with those of the National Research Council’s (2003) conclusions regarding polygraph accuracy, and provide additional support for the validity of polygraph testing when conducted in accordance with APA Standards of Practice.”
American Polygraph Association. (n.d.). Polygraph Validity Research from https://www.polygraph.org/polygraph-validity-research
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT NOW
Major credit cards accepted

Please consider referring our services to your colleagues!
We would really appreciate it if you would share this page ↴
